Step 1 : Create Database
Start MySQL server (or any DB server) and create a database called UserReg. For MySQL users , you can use phpmyadmin that comes with XAMPP or WAMP to do this quickly
Step 2 : Create a Persistence Unit
- Right click on source packages in your project and select "New > Persistence Unit". You'll see a window similar to the screen shot below;
2. Type in the persistence unit name as shown above.
3. Next you need to create a data source. This is the database you created earlier in step 1 above. Select the Data Source drop down and click "New Data Source". You'll see a window similar to the one shown below.
4 . Type in the JNDI Name as jdbc/userreg . In the Database Connection drop down, select "New Database Connection". You'll see a window similar to the one shown below.
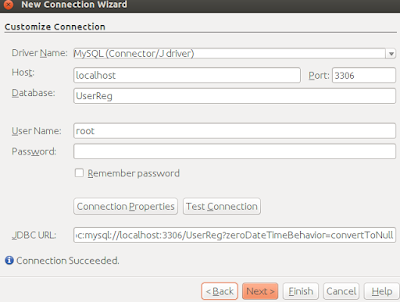
5 . Since we are using MySQL DBMS, select "MySQL(Connector/J Driver) Driver" and click Next. You'll see a window similar to the one shown below.
6. Enter the name of the database you created in Step 1 Above. In this case "UserReg" , enter user name and password of your database and click "Test Connection". On successful connection you'll see a window similar to the one below.
7 . Click Finish . This should take you back to the window in step 3 above. You'll see your database connection URL is selected on the Database connection drop down as shown below.
8. Click Ok to return to the persistence wizard window as shown below.
9 ) Click finish to complete and close the persistence unit wizard.
Congrats ! You've successfully configured a data source for your application.In the next tutorial, ill show you how to write code that will persist/insert users into your new DB.